1. GENERAL INFORMATION ON STRUCTURED FINANCE
Securitization is generally defined as the process of pooling receivables that will generate future cash inflows and issuing securities backed by these pools to be sold to third-party investors. Lease certificates (Sukuk) transactions, on the other hand, are primarily based on partnership and profit-and-loss sharing principles. Considering sukuk practices as well, the definition of securitization can be expanded as the process through which existing tangible assets, receivables, or even non-liquid project-based assets are converted into negotiable and liquid securities, thereby being offered to investors.
Through Structured Finance (SF) instruments, companies in need of funding can access new and more cost-effective financing sources and benefit from more efficient portfolio management. Structured Finance transactions enable companies to discount future cash flows to the present, reorganize their balance sheets in a more desirable form, and reach more liquid positions through the funds obtained.
One of the most important characteristics of SF transactions is that multiple institutions and entities take end-to-end roles within the securitization process. Accordingly, a range of specialized functions emerge across the structural components of the transaction. Depending on the characteristics of the SF product, the type of issuance, and applicable legal regulations, the relevant parties may vary; however, in the broadest sense they include:
• Originator
• Servicer
• Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV)
• Asset Lease Company
• Founder
• Guarantor
• Promoter
• Custodian
• Trustee
• Collateral Agent
• Cash Manager
• Payment Institutions
• Intermediary Institutions
• Insurance Mechanisms for Debtors and Investors
• Rating Agencies
• Investment Banks
• Investors
2. RISKS RELATED TO STRUCTURED FINANCE ISSUANCES
SF issuances encompass numerous internal and external risk elements that may vary depending on the nature and type of the underlying pool or fund portfolio. Among the principal risk types are credit risk, which reflects the possibility of delays or defaults in principal and interest payments; interest rate risk, which affects the demand for investment instruments; prepayment risk, which arises when debtors within the pool of receivables or loans make early repayments that may disrupt the functionality of the cash flow mechanism; concentration risk, which occurs when receivables or loans in the pool exhibit clustering based on specific criteria; dilution risk, which refers to potential cash concessions granted on receivables; residual value risk, typically observed in pools or portfolios composed of receivables originating from vehicle leasing activities; commingling or redirection risk, which may occur during the transfer, servicing, or assignment of receivables; operational risk, resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, employees, clients, third parties, or systems, or from external events that lead to erroneous or fraudulent transactions; legal risk, stemming from changes in legislation or regulatory requirements, or from contractual alterations between parties; and counterparty risk, which may emerge when the repayment obligations of the issuance become operationally dependent on counterparties or other supporting entities.
In some SF practices, since receivables or loans are transferred outside the originator’s balance sheet, a Moral Hazard risk may arise if the originator fails to exercise sufficient diligence and prudence. Alongside this moral hazard, an Adverse Selection phenomenon may also occur. This arises when the criteria for selecting receivables or loans to be transferred to the pool or fund are not clearly and accurately defined, resulting in the concentration of either low-quality or high-quality receivables and thereby introducing differing levels of risk.
3. CREDIT ENHANCEMENTS
In issuance processes, credit enhancement mechanisms are required for various reasons such as mitigating disruptions in cash flow and reducing credit risk, strengthening the investor’s decision-making process, achieving a higher rating level for the security, enhancing its marketability and overall value, and increasing investor demand for the issuance. Credit enhancement mechanisms are classified as internal and external, where internal mechanisms consist of those provided by the issuing institution itself, and external mechanisms are elements supplied by third parties. In cases where cash flow constraints occur, the Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) to which the underlying assets have been transferred first resorts to these mechanisms to tolerate the cash flow shortfall and may subsequently utilize collateral linked to the receivables to secure collections. The most common internal or external credit enhancement mechanisms include overcollateralization, subordination, recourse arrangements, replacement of non-performing receivables with performing ones, the establishment of a debt service reserve account funded by cash advances prior to issuance, excess spread between portfolio yield and coupon/principal payments, letters of guarantee, bank guarantees, and insurance instruments.
4. SEGMENTATION OF RATING METHODOLOGIES
In the field of SF, issuances may differ for a variety of reasons. Accordingly, JCR ER considers it important, in compliance with the relevant legal and regulatory framework, to subdivide this area into subcategories based on the type of issuance and the nature of the underlying assets, in order to ensure a more effective and comprehensive analysis.
Within this scope, the assessment of the repayment capacity of securities in SF products is not conducted solely on the basis of the originator’s probability of default. This results from the inherently complex structure of structured finance, which, by its nature, incorporates multiple components within a single transaction. Considering these aspects, SF rating processes are fundamentally classified into three main categories:
• Asset-Backed or Mortgage-Backed Securities (ABS/MBS),
• Covered Bonds (CB),
• Lease Certificates (Sukuk).
The rating methodologies adopted in these processes are selected appropriately according to the specific structure of the transaction and the characteristics of the underlying assets. Given that the scope, structure, and legal frameworks of such issuances differ -depending on whether the underlying assets are transferred off-balance sheet or to a fund- this segmentation has been established.
Furthermore, since assessing the underlying assets within the main segments based on differentiated criteria such as product characteristics and risk profiles provides a more accurate evaluation, these main segments have been further divided into subsegments, thereby rendering the assessment criteria more specialized in structure.
The relevant subsegments are presented below.
4.1 Asset-Backed or Mortgage-Backed Securities (ABS/MBS)
4.1.1 Asset-Backed Securities (ABS)
Within the framework of the Asset-Backed Securities (ABS) methodology, which refers to securities issued against assets to be acquired by an Asset Finance Fund or a Mortgage Finance Institution, eight sub-models have been established based on the type of underlying asset:
• Receivables from Agricultural Activities / Agricultural Loans
• Receivables from Vehicle Purchases / Auto Loans
• Trade Receivables
• Commercial Loans
• Consumer Loans
• Credit Card Receivables
• Receivables from Aircraft Purchases / Aircraft Loans
• Receivables from Marine Vessel Purchases / Ship Loans
4.1.2 Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS)
Within the framework of the Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS) methodology, which refers to securities issued against assets to be acquired by a Housing Finance Fund or a Mortgage Finance Institution, two sub-models have been established based on the type of underlying asset:
• Residential Mortgage-Backed Securities (RMBS)
• Commercial Mortgage-Backed Securities (CMBS)
4.2 Covered Bonds (CB)
Within the framework of the Covered Bonds (CB) methodology, which refers to a type of capital market instrument structured as a debt security issued under the general obligation of the issuer and collateralized by cover assets, two sub-models have been established based on the nature of the collateral:
• Asset-Covered Bonds
• Mortgage-Covered Bonds
4.3 Lease Certificates (Sukuk)
Within the framework of the Lease Certificates (Sukuk) methodology, which refers to securities issued by an Asset Lease Company to finance various types of assets or rights and which entitle their holders to income generated from such assets or rights in proportion to their ownership, six sub-models have been established:
• Ownership (Ijara)
• Management Agreement (Wakala)
• Trading (Murabaha)
• EPC (Engineering, procurement and construction) Contract (Istisna)
• Partnership (Mudaraba and Musharaka)
• Hybrid Sukuk
5. RATING METHODOLOGY FRAMEWORKS
The rating of capital market debt instruments represents an opinion regarding the likelihood of timely and full payment of principal and interest on the relevant security. In this context, the repayment capacity of a security cannot, by nature, be considered entirely independent from the probability of default of its issuer.
However, in SF issuances, the assessment of a security’s payment capacity is not based solely on the originator’s probability of default. This is due to the inherently complex structure of structured finance transactions, which by their nature bring together multiple interrelated components.
Considering these factors, the criteria applied and the areas of analytical emphasis within the SF rating methodology vary depending on the type of issuance (for instance, Asset-Backed Securities [ABS], Covered Bonds [CB], and Lease Certificates [Sukuk]) as well as the characteristics of the underlying assets or rights (e.g., auto loans/receivables, agricultural loans/receivables, partnership sukuk or trading sukuk).
Accordingly, the issuances subject to rating are classified as follows.
5.1 Asset-Backed Securities (ABS) and Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS)
Applications of Asset-Backed Securities (ABS) serve as an instrument to strengthen capital structures, obtain funding at favorable costs, address mismatches between assets and liabilities, and create more liquid balance sheets, while also contributing to the overall efficiency of the financial system. Within this framework, such issuances facilitate the development of new investment instruments that enhance liquidity for receivables or loans, thereby channeling financial resources into the economy and improving cash circulation.
In asset-backed securitization (ABS) transactions, the originator transfers the pool of assets or loans to a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV). Following this transfer, the SPV issues securities linked to the established asset pool or fund portfolio and offers the associated future cash flows to investors. The proceeds obtained from investors provide liquidity for the originator, as the receivables or loans transferred off its balance sheet are converted into cash, thereby creating a new source of funding. Transactions structured in this manner based on receivables or loans are referred to as Asset-Backed Securities (ABS), while those based on mortgage loans are termed Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS).
Each structured finance issuance carries its own specific characteristics, and the associated costs vary depending on the nature and type of the underlying assets, the issuance structure, the originator’s asset-liability composition, the size of the pool, and the level of credit enhancement.
The diagram below illustrates the ABS issuance process and the parties involved.
Figure 1: ABS Issuance Process
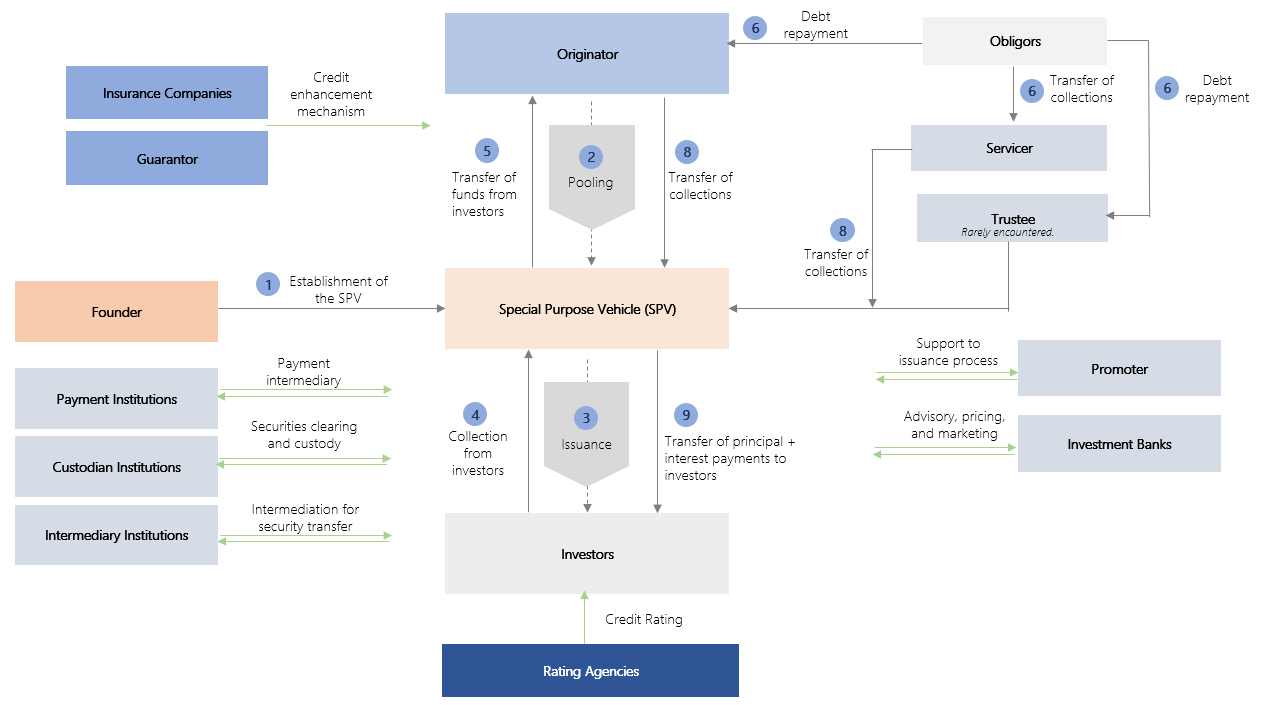
Note: The figure above illustrates the ABS issuance process in its most comprehensive form; however, in practice, not all of the parties shown may be involved depending on the nature of the issuance.
In ABS issuances, the receivables or loans held on the originator’s balance sheet are transferred to the SPV, thereby being removed from the originator’s assets and financial statements. The purpose of this transaction is to ensure that the cash flows generated from the collection of these receivables or loans are allocated exclusively to the holders of the asset-backed securities. As a result, the securities become insulated from potential negative changes in the financial condition of the originator, and the receivables within the pool, from another perspective, acquire the nature of collateral serving a risk-mitigation purpose.
Compared to traditional bond issuances (Where the financial soundness and repayment capacity of the issuing entity are key determinants) asset-backed securities are relatively less exposed to such dependence, thereby making these instruments more attractive than conventional debt products.
The structured finance mechanism operates through several key transaction elements, including pooling, tranching, and de-linking. Different credit rating grades are assigned to each tranche according to its investment quality. The waterfall structure applied in securitization dictates that amortization proceeds from the top tranche downward, meaning no lower-ranking tranche receives payments until the senior tranche has been fully redeemed. Consequently, if collection problems arise and the expected cash flow is not realized, investors holding the lowest tranches may face the risk of non-payment.
Funds collected from receivable payments may be managed through either pass-through or pay-through mechanisms. In the pass-through method, payments to investors are directly aligned with the maturities of the cash flows generated by the pool, ensuring immediate transfer to ABS holders without retention within the fund. In contrast, under the pay-through structure, cash flows may be retained within the fund until the maturities predetermined by the Fund Board, as outlined in the prospectus or issuance document.
Within the ABS framework, analyses are conducted across several sub-categories, focusing on the quality of the originator and servicer, the quality of the fund portfolio and debtor creditworthiness, SPV robustness, other transaction parties, and the payment and cash-flow structure. The outcomes of these assessments, combined with macroeconomic and sectoral evaluations, are consolidated in a matrix to determine the Baseline Risk Profile (BRP) of the issuance. Following the establishment of the BRP, additional factors -referred to as modulators- are applied. Each criterion evaluated within the modulator assessment may adjust the base risk profile upward or downward. After reflecting the impact of these modulators, the Stand-Alone Risk Profile (SARP) is derived. Subsequently, support assessments that consider group and public-sector support elements, along with ESG criteria, are incorporated into the analysis to determine the SFR rating of the issuance. The final SFR rating may be subject to upward or downward override based on the decision of the Rating Committee. The process is summarized in the figure below.
Figure 2: ABS-MBS Methodology Framework
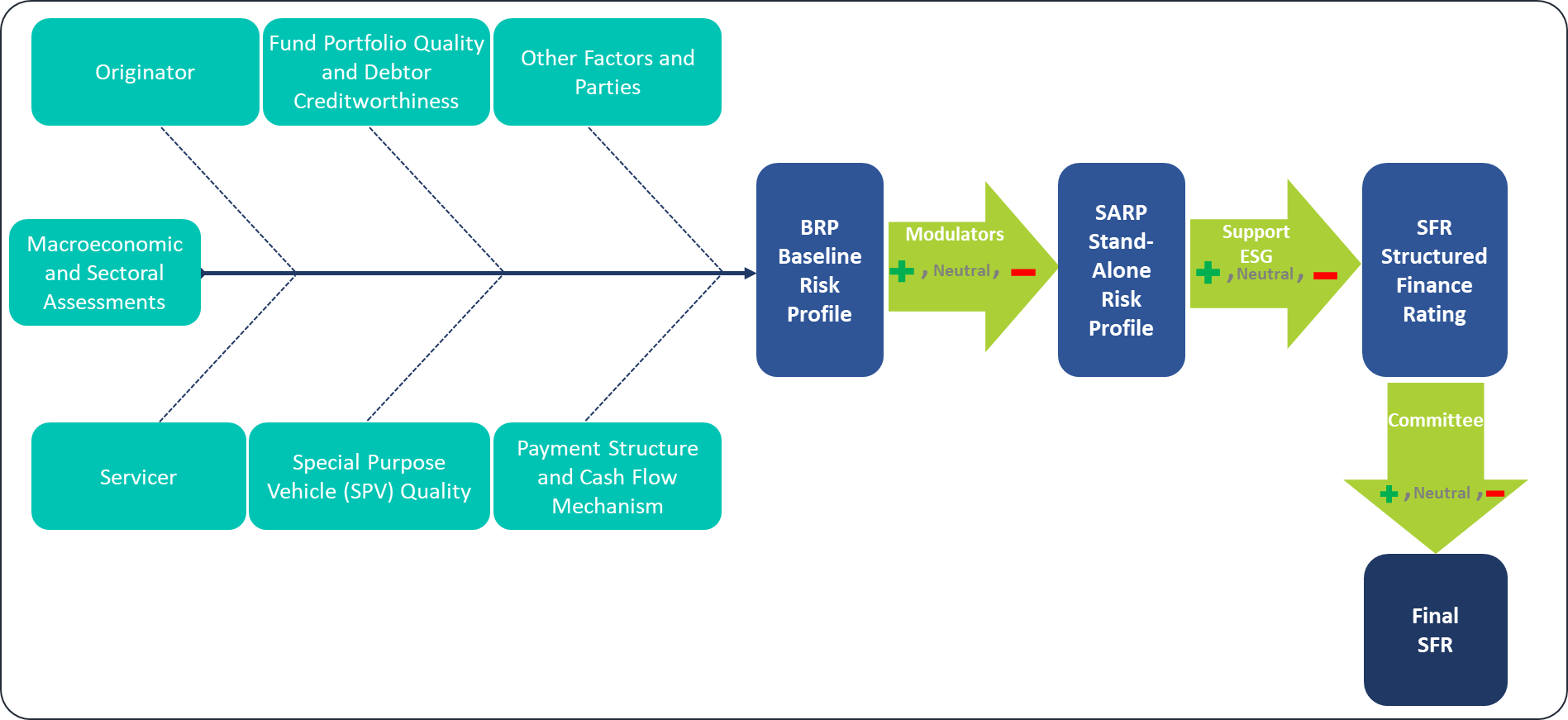
5.2 Covered Bonds (CB)
A Covered Bond (CB) is a type of capital market instrument structured as a debt security that represents the general obligation of the issuer and is collateralized by a pool of cover assets. Two types of Covered Bonds may be issued: Asset-Covered Bonds (ACB) and Mortgage-Covered Bonds (MCB).
Covered Bond structures serve as instruments that not only help preserve the size of the issuer’s balance sheet and positively contribute to the liquidity coverage ratio -thereby enhancing lending capacity- but also improve the overall efficiency of the financial system. Within this context, such issuances contribute to the creation of new investment instruments, increasing the liquidity of receivables or loans, injecting financial resources into the economy, and supporting greater cash circulation.
The diagram below illustrates the Covered Bond issuance process and the parties involved.
Figure 3: Covered Bond Issuance Process
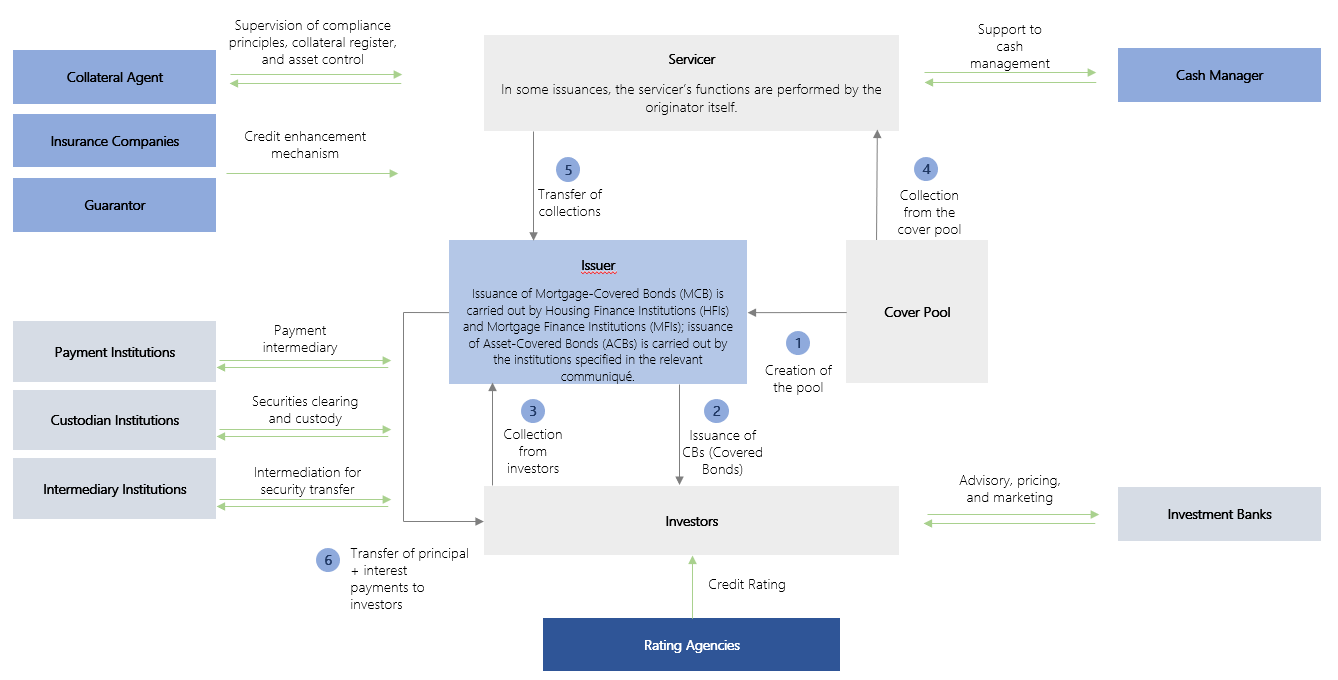
Note: The figure above illustrates the CB issuance process in its most comprehensive form; however, in practice, not all of the parties shown may be involved depending on the nature of the issuance.
Asset-Covered Bonds (ACB) and Mortgage-Covered Bonds (MCB) are debt instruments issued with underlying assets serving as collateral. The assets pledged as collateral constitute what is known as the cover pool. Unlike Asset-Backed Securities (ABS), these assets remain on the issuer’s balance sheet. However, within the operation of Covered Bonds (CB), the assets in the cover pool are ring-fenced from the issuer’s other assets to provide protection. This structural safeguard aims to ensure additional security for investors in the event of the issuer’s insolvency. In case of default by the issuer, Covered Bond investors have dual recourse, meaning they have a claim both on the proceeds generated by the assets in the cover pool and on the issuer itself.
Although assets within the CB structure are segregated through registration in a cover register, they remain on the issuer’s balance sheet. This means that the issuer’s control and responsibility over these assets continue, which also exposes the CB issuance to potential risks and fluctuations in the issuer’s financial condition. Therefore, the assessment of the issuing entity is considered highly significant in the rating of the issuance.
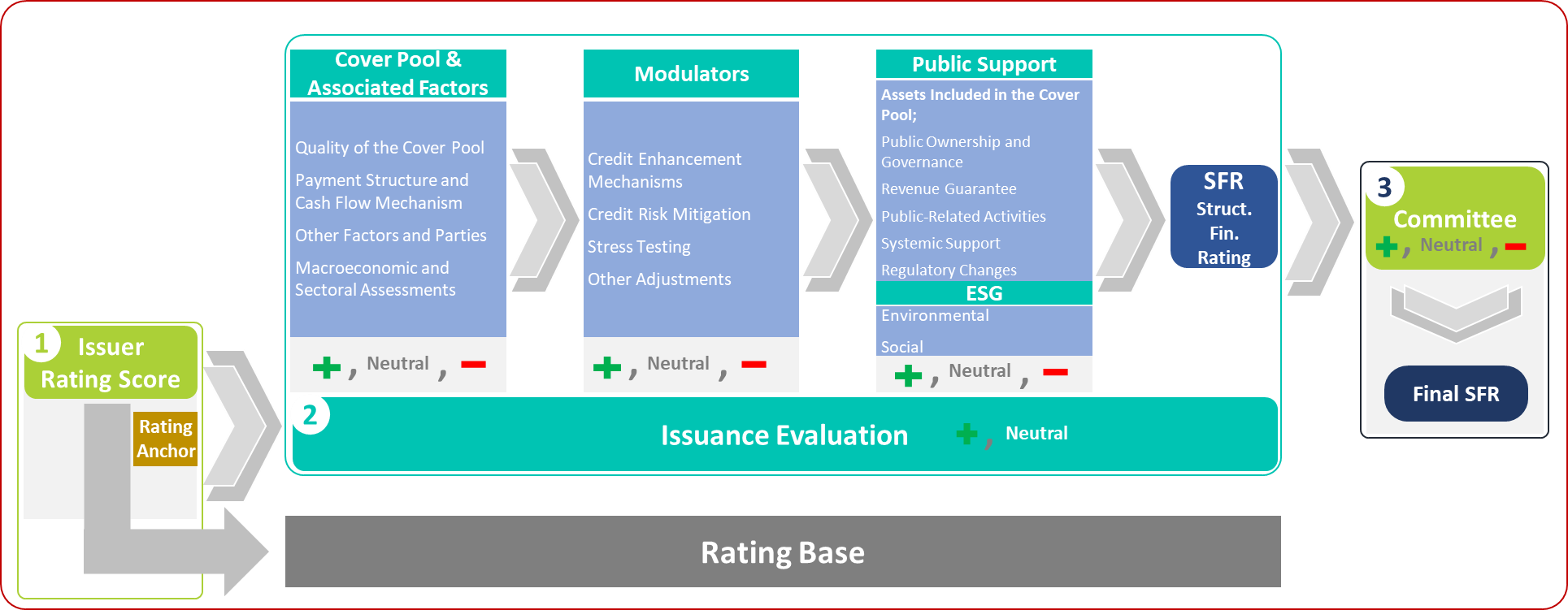
The CB methodology is built upon the application of the most suitable existing JCR ER methodology corresponding to the issuer’s line of business in order to determine the rating of the CB issuer. The issuer’s rating serves as the anchor rating for the CB issuance. After establishing this anchor rating, the quality of the cover pool is analyzed, encompassing subcategories such as borrower characteristics, concentration risk, sensitivity to external variables, liquidity profile, Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratio, and asset characteristics. The analysis is then expanded by examining the payment structure, cash flow mechanism, all participating parties, and other related factors.
In addition to these assessments, macroeconomic and sectoral evaluations are considered to complete the analysis phase relating to the cover pool and associated factors. The next stage involves the modulator assessments, which include evaluation of credit enhancement mechanisms, stress test outcomes, and credit risk mitigation techniques. Prior to the committee evaluation, public support assessment is conducted with reference to the receivables within the cover pool, followed by ESG assessments, leading to the determination of the issuance’s SFR rating. At each of these stages, the resulting SFR rating may move upward or downward relative to the issuer’s anchor rating; however, the final SFR rating cannot be lower than the issuer’s own rating. The final rating may still be subject to upward or downward override based on the Rating Committee’s decision. The overall process is summarized in the figure below.
Figure 4: Covered Bond Methodology Framework
5.3 Lease Certificates (Sukuk)
One of the most common instruments in the Islamic financial system, Sukuk represents ownership of an asset or the right to benefit from it for a defined period. It provides investors with regular fixed or variable returns and constitutes an interest-free capital market instrument that can be traded in secondary markets.
Developed as an alternative investment instrument to conventional interest-bearing financing methods, Sukuk generates returns in the form of rental income or profit share, in line with Islamic principles that prohibit interest (riba). Unlike conventional securities, Sukuk investors do not own an entire portfolio but instead share in the income generated by a specific asset or group of assets that has been identified and purchased by an Asset Lease Company (ALC).
In Türkiye, Sukuk largely corresponds to lease certificates as defined under the Capital Markets Board’s (CMB) Lease Certificates Communiqué. According to this regulation, lease certificates are securities issued by an Asset Lease Company for the purpose of financing any type of asset or right, entitling their holders to a proportional share of the income derived from such assets or rights.
Compared to other capital market instruments, lease certificates currently attract relatively limited investor interest and operate within an underdeveloped market structure. To protect investors and prevent potential misconduct by issuers, various regulatory safeguards have been introduced.
One such measure stipulates that until the Sukuk reaches maturity, the assets and rights held in the ALC’s portfolio may not be disposed of, pledged, used as collateral, seized for public receivables, included in bankruptcy estates, or subjected to injunctions-except for collateralization purposes within the issuance structure. Furthermore, this restriction remains valid even if the management or supervision of the ALC is transferred to a public institution.
Through Sukuk issuance, the originator primarily converts assets or rights on its balance sheet into funding sources, thereby accessing low-cost financing. In addition, the issuance allows for the expansion and diversification of the investor base and provides certain tax advantages. Lease certificates may be issued through public offering or private placement, the latter conducted either as a qualified investor placement or an allocated (bespoke) sale.
The steps and procedures in Sukuk issuance vary according to the type of lease certificate being issued. Factors such as the transfer of assets, the management and valuation of the assets or rights, and whether the issuance relates to a specific project or enterprise differ depending on the Sukuk structure.
The diagram below illustrates the Sukuk issuance process and the parties involved.
Figure 5: Sukuk Issuance Process
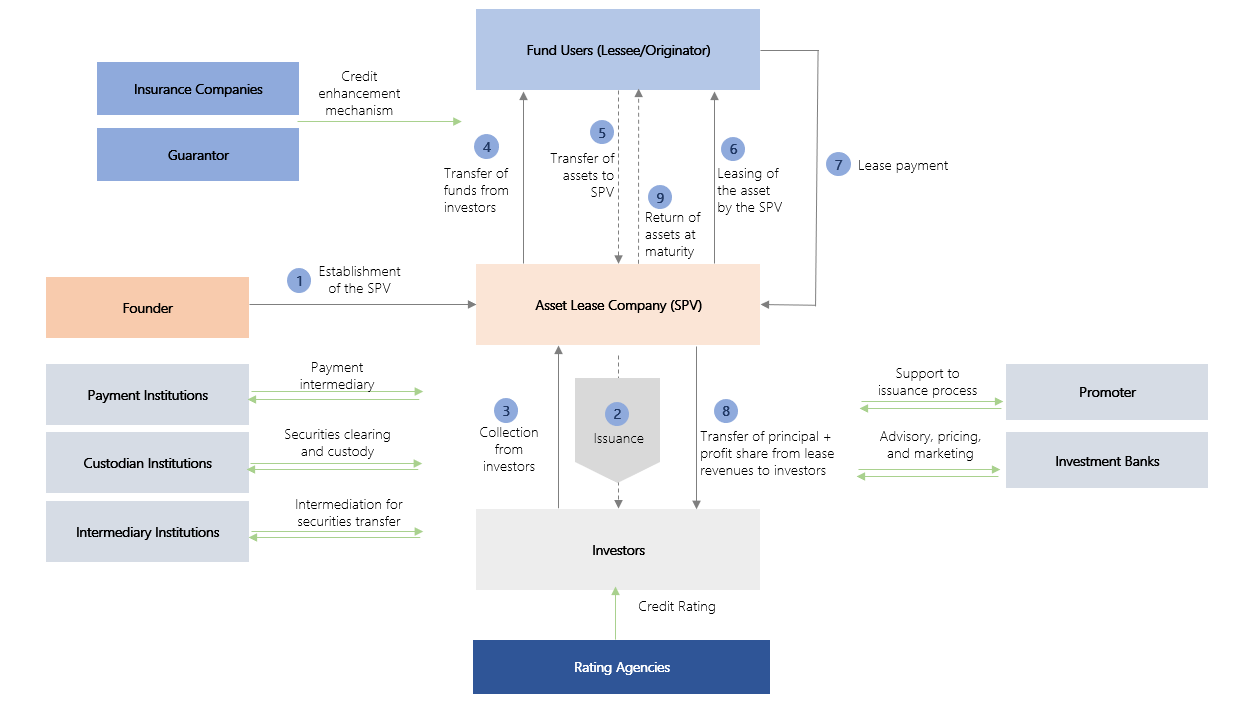
Note: The figure above represents the Sukuk issuance process in its most comprehensive form, corresponding to the detailed structure of an ownership lease certificate. In practice, the parties involved may vary depending on the nature of the issuance, and the flow, participants, and terminology may differ according to the specific type of Sukuk.
In accordance with the Communiqué, six types of lease certificates (Sukuk) may be issued depending on the nature of the underlying asset or right, including ownership (Ijara), management agreement (wakala), trading (murabaha), partnership (mudaraba or musharaka), EPC (engineering, procurement and construction) Contract (Istisna) and hybrid structures combining more than one type.
A lease certificate (Sukuk) is a security issued by an Asset Lease Company (ALC) for the purpose of financing various assets and rights, granting its holders entitlement to a proportional share of the income derived from such assets or rights. In its operational structure, there are generally three parties involved: the originator or fund user who owns the asset or right subject to issuance, the Asset Lease Company (ALC), and the Sukuk investors. Depending on the type of lease certificate, the funds raised may be transferred to projects through EPC contract or partnership agreements, or used in trading, lease-sale, or management agreements. The income generated from these activities is distributed to Sukuk holders in proportion to their ownership shares. At maturity, the underlying assets or rights are sold to the originator or to third parties, thereby concluding the issuance. Each type of lease certificate may be based on different underlying assets or rights, involve different participants, and follow distinct issuance mechanisms.
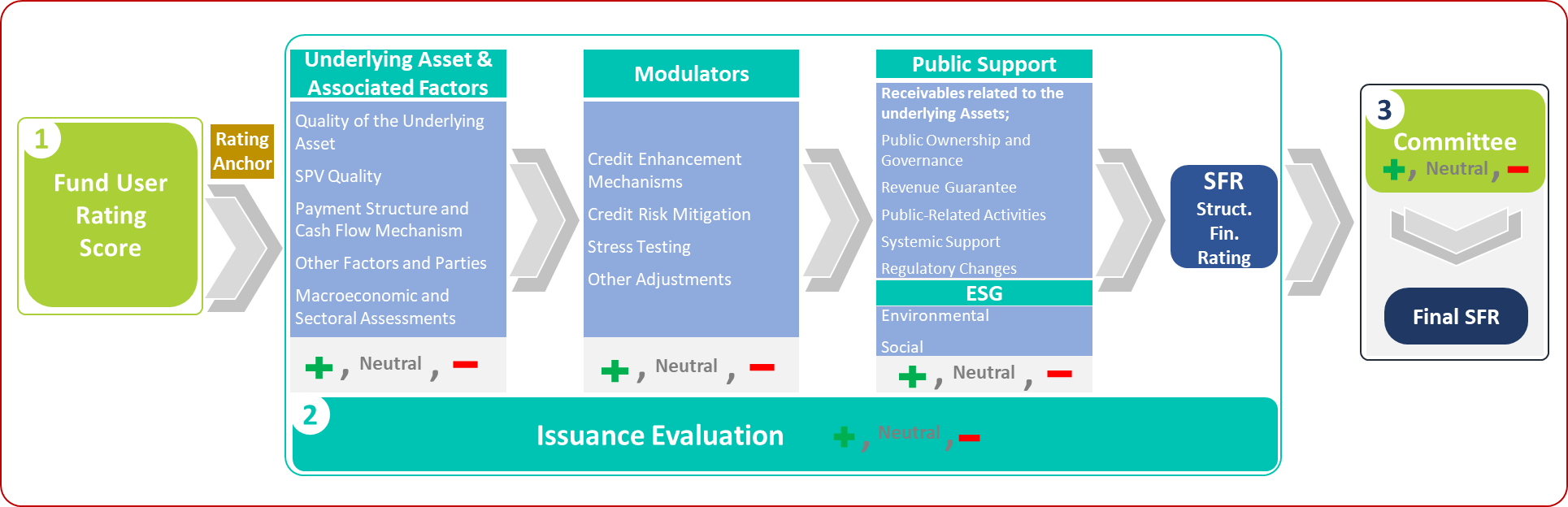
The Sukuk Methodology begins with the rating assessment of the fund user, which is conducted using the most appropriate existing methodology within the institution based on the nature of the fund user’s operations. After determining the fund user’s rating, the quality of the underlying asset is analyzed with respect to sensitivity to external variables, structural features, and the characteristics of the related asset, project, or enterprise. Following this, the quality of the Asset Lease Company (ALC) is evaluated. The analysis is further deepened through the examination of the payment structure, cash flow mechanism, all involved parties, and other relevant factors. In addition, macroeconomic and sectoral analyses are incorporated to complete the evaluation stage concerning the underlying asset and related aspects. After establishing the fund user’s rating as the base, all subsequent assessments may affect the rating positively or negatively. The next stage involves the modulator assessments, which primarily focus on credit enhancement mechanisms, stress testing, and credit risk mitigation techniques. Before the committee evaluation, a public support assessment is conducted considering the receivables related to the underlying assets, followed by ESG assessments, leading to the determination of the SFR rating of the issuance. At each stage, the rating may move upward or downward relative to the fund user’s rating; however, the final SFR rating is subject to override -either upward or downward- by the decision of the Rating Committee. The overall process is summarized in the figure below.
Figure 6: Sukuk Methodology Framework
6. SURVEILLANCE PROCESS
The validity of the ratings assigned by JCR ER to Structured Finance (SF) issuances is determined in alignment with the maturity date of the instruments, and the assigned ratings expire upon the completion of redemption. Although the initial rating stage is of great importance, the dynamic nature of SF transactions -being exposed to various factors such as collection performance, reinvestment activities, and macroeconomic fluctuations- necessitates continuous monitoring. Accordingly, the SFR ratings assigned to SF issuances are reviewed regularly until maturity, and rating revisions may be made when deemed necessary.
Within the framework of the JCR ER Structured Finance methodology, the surveillance process is carried out according to differentiated criteria based on specific maturities and relevant conditions. Fundamentally, SF issuances are monitored on a monthly basis using a set of criteria, while quarterly monitoring cycles are conducted using a broader and more holistic set of indicators. Furthermore, the criterion structure defined according to the issuance type and the diversity of underlying assets in the SF methodology is also adopted in the surveillance process. These criteria primarily focus on changes observed after the issuance.
In the case of Asset-Backed Securities (ABS), JCR ER’s surveillance process takes into account specific criteria grouped under key categories such as the quality of the originator, the servicer, the quality of the fund portfolio, debtor creditworthiness, and other transaction-related factors. From a broader perspective, the surveillance process for ABS includes the assessment of whether the originator or servicer has been subject to investigations or inquiries by supervisory or governmental authorities, the evaluation of any ongoing or anticipated lawsuits, and the identification of any adverse findings in interim independent audit reports. Additionally, it focuses on potential changes in the originator’s creditworthiness and the effects of ongoing or potential mergers and acquisitions.
Under the “fund portfolio quality and debtor creditworthiness” category, natural disasters or catastrophic events, unfavorable developments in economic conditions or agricultural productivity (such as crop disease, pest infestation, human error, or drought), and changes in insurance-related subsidies, incentives, or credit campaigns are examined to determine their impact on the cash flow and the asset pool. The cut-off points for weighted average remaining maturity are differentiated based on the underlying asset and model and are analyzed within the relevant category.
In the context of Covered Bonds (CB), in addition to factors such as weighted average remaining maturity, natural disasters, catastrophic events, and changes in insurance or credit-related incentives and campaigns, other criteria such as nominal value matching, cash flow matching, and net present value (NPV) matching are also considered. Under the “other factors and parties” category, most of the criteria applied in the ABS framework are also incorporated into CB surveillance.
In the context of Lease Certificates (Sukuk), in addition to the relevant criteria adopted from other areas, additional considerations include legal status reports, post-issuance disputes arising from Shariah (fatwa) interpretations, significant amendments to previous contracts (such as lease, usufruct, sale, real estate sale promise, agency, and insurance agreements) that could affect cash flow, and changes in the quality of the asset portfolio subject to management contracts.

